
Mind wandering is linked to psychopathological conditions, such as anxiety and depression, as it can contribute to rumination and negative thoughts. Mindfulness practices, on the other hand, aim to reduce mind wandering and have shown promise in improving mental well-being by promoting present-moment awareness and emotional regulation.
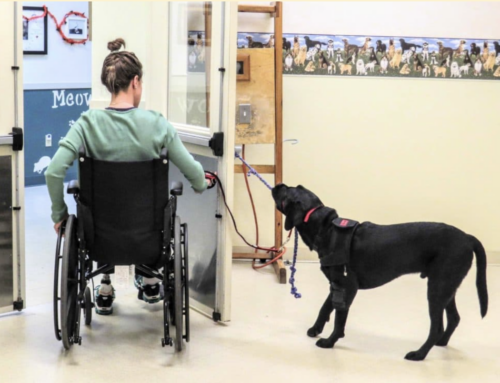
This article discusses the therapeutic benefits of pets on human health, emphasizing their role in enhancing physical activity, improving mood, and providing emotional support. Through personal experience and scientific research, it underscores the transformative impact of pet ownership on individuals’ well-being.

This article delves into the profound impact of traumatic childhood experiences on an individual’s cognition and memory. It discusses how childhood trauma can lead to memory retrieval problems, such as dissociative amnesia, and impairments in working memory, emphasizing the need for effective interventions and therapeutic approaches to assist survivors in improving their mental well-being.

The article discusses how lying can lead to the subconscious reconstruction of memories, causing individuals to believe their own falsehoods and blur the line between truth and deception. It explores factors like fabrication inflation, the anchoring effect, and motivated forgetting, highlighting the malleability of memory and the potential consequences of false memories resulting from deceptive acts.

In third grade, my mom handed me a frail copy of Are You There god? It’s Me, Margaret (AYTGIMM), by Judy Blume. The pages were discolored, the binding hanging on by a thread (literally). The state of the book mirrored my feelings after having “the pube …

Every day, we encounter numerous faces of diverse genders, ages, and races, and our ability to identify them accurately is crucial. Recognizing the limitations of both human and Artificial Intelligence facial recognition systems, this article aims to explore the causes and implications of facial recognition failures.
4.4% of Adults in the United States are clinically diagnosed with ADHD, and 32.7% of ADHD adults rely on stimulants for treatment. However, in 2022 the FDA announced that there was a drug shortage, which also impact Adderall production. Adderall is the most common medication prescribed to ADHD patients and a lack of this medicine leads to both physical and mental withdrawal effects.

What does an analogy between origami and the mind tell us about the current state of cognitive science?

How do we “rest on purpose”? Let’s start with redefining the relationship between rest and work.

The weapon focus effect can help us understand how people remember highly emotional events. Could this change how we think about eyewitness testimony?

What do older cognitive models of categorization tell us about memory that state-of-the-art neural networks do not? The difference between past and present is not just one of performance, but also of psychological insight.
Have you ever wanted to train your brain? Neurofeedback has been claimed to aid in the treatment of several disorders and cognitive patterns such ADHD, depression, epilepsy, and others–particularly conditions resistant to treatment.

One characteristic of autism that has been scarcely researched is manifestation differences between biological sexes, with damaging consequences. Moreover, male social rejection is much easier to detect than the more passive female exclusion in the autism population.

Non-sleep deep rest (NSDR) and Yoga Nidra are two trendy practices that are typically grouped together because they are both utilized to reduce stress, achieve deep relaxation, and induce sleep. In this blog post, I will outline the empirically demonstrated benefits and future potentials of Yoga Nidra.

Have you ever questioned why some information is recalled better than others? Research has shown that people have a tendency to predict a higher memory and better recall emotional information. Read about the potential mechanisms that could explain the influence of emotion on our beliefs and memory.

What role does failure play in learning? While students tend to be aversive to failure, it plays a natural and important role in the learning process.

Today, we talk about the National Science Foundation and our experiences with applying for fellowships and working with the NSF.

Today we are joined by Dr. Janet Tomiyama from ucla to talk about the issues that prevent dieting success, including stress and stigma.

Today, we are joined by Dr. Jennifer Silvers from UCLA to talk about emotional regulation and early life stress.
We had a discussion today with Dr. Adriana Galvan about how studying adolescent brains and the implications it has on how we understand risk taking.

Do you learn better by your eye or ear? Research has shown that memory is better for information we learn visually than aurally. Yet, to ensure optimal learning one must consider the use of multisensory integration, or the simultaneous use of both visual and auditory aids.